Money laundering is one of the major threats to the financial system because it can reduce public trust, disrupt economic balance, and provide space for organized crime activities.
At the global level, this practice can disrupt economic stability and complicate the implementation of state budget policies.
In today’s digital era, money laundering is increasingly developing with the existence of cryptocurrency, which is often used illegally because of its anonymous nature.
Therefore, it is important to understand and address this threat in order to protect economic stability and keep the financial system safe.
What is Money Laundry?

Money laundering is the process of laundering money or hiding or disguising the origin of funds obtained illegally to make it look like the result of legitimate activities.
Usually, this activity is carried out through various complex financial transactions to make it difficult to trace the original source.
In Indonesia, money laundering is regulated through Law No. 8 of 2010 concerning the Prevention and Eradication of the Crime of Money Laundering.
Internationally, the legal basis for this practice refers to the 1988 UN Vienna Convention, which establishes a global framework for combating money laundering, especially those related to drug trafficking and other cross-border crimes.
Furthermore, money laundering has broad negative impacts, such as undermining economic stability, encouraging the development of organized crime, and weakening confidence in the financial system.
In addition, this practice also reduces the effectiveness of government financial policies, thereby hampering healthy economic growth.
Money Laundering Stages
The money laundering stages end when the funds from illegal activities are successfully entered into a financial system that is considered legal.
Based on an explanation from the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), here are three stages that usually occur, namely:
Placement: This stage involves separating money from the criminal activity that is its source, usually by entering it into the financial system or changing it into another form.
Layering: At this stage, various transactions are carried out to disguise the origin of the funds so that it is difficult for authorities to trace them.
Integration: The final stage where the laundered money is re-introduced into the economy with the appearance of coming from a legitimate source so that it can be used by the perpetrator without arousing suspicion.
It is important to note that the stages above do not always occur linearly. This is because in some cases, the perpetrator can skip or repeat one of the stages, depending on the situation and the laundering method used.
This flexibility is often used to avoid detection and maximize the effectiveness of money laundering.
Money Laundering Modus Operandi
Money laundering is carried out in various ways to hide the origin of illegal funds. The methods used can vary, depending on technological developments and changes in regulations.
In general, money laundering modes can be divided into two main categories, namely traditional modes that rely more on manual methods and modern modes that utilize the latest technology.
The following are some modes that are often used in money laundering practices that are important to know and be aware of.
1. Traditional Mode
Dividing funds into several accounts: The perpetrator will divide the proceeds of crime into several accounts to avoid suspicion.
Fictitious buying and selling transactions: The perpetrator will carry out buying and selling transactions that never actually happened to disguise the origin of the funds.
Use of shell companies: The perpetrator will use shell companies that do not carry out real business activities as a medium for money laundering.
Investment in luxury goods: The perpetrator will invest money in luxury goods such as vehicles, property, or jewelry to change the form of funds into assets that are difficult to trace.
2. Modern Mode
Use of digital financial technology: Perpetrators utilize digital financial technology such as e-wallets or money transfer applications to obscure transaction traces.
Utilization of cryptocurrency for anonymous transactions: Perpetrators will use cryptocurrency that allows anonymous transactions to occur and is difficult for authorities to track.
Trading through the dark web market: Perpetrators will conduct illegal trading through the dark web market, which is often a place for unrecorded transactions.
Money Laundering Regulation and Prevention
Basically, preventing money laundering requires a clear legal framework and effective implementation at the national and global levels. The following are the regulations and preventive measures that apply in Indonesia and globally.
1. In Indonesia
Law No. 8 of 2010 regulates the prevention and eradication of money laundering crimes, which provides a legal basis for efforts to combat this practice.
Institutions such as PPATK (Financial Transaction Reports and Analysis Center) play an important role in monitoring suspicious financial transactions, while OJK (Financial Services Authority) is tasked with supervising financial institutions and ensuring compliance with existing regulations.
2. Global
FATF (Financial Action Task Force) sets international standards in preventing money laundering through AML (Anti-Money Laundering) guidelines adopted by many countries around the world.
KYC (Know Your Customer) is a regulation that requires financial institutions to recognize and verify customer identities to prevent misuse of the system for money laundering.
Technology also plays an important role in preventing money laundering, with the implementation of blockchain transaction monitoring, the use of AI (Artificial Intelligence) to detect suspicious transaction patterns, and big data to analyze large transactions efficiently.
Money Laundering in Crypto
With its anonymity and ability to transact across borders, cryptocurrency has become a vulnerable tool for money laundering.
Without adequate regulation in some countries, criminals can exploit loopholes to hide the source of illegal funds.
Why is Crypto Vulnerable to This?
Anonymity and Cross-Border Transactions: Cryptocurrency offers a high level of anonymity, allowing criminals to hide their identities. In addition, transactions can be conducted without geographical restrictions, making it easy for perpetrators to move funds between countries without detection.
Lack of Regulation in Some Countries: In some regions, cryptocurrency regulations are weak or even non-existent. This provides loopholes for money launderers to exploit the unsupervised system.
Modes in the Crypto World

Mixers and Tumblers: Services like mixers and tumblers are used to obfuscate transaction traces by combining funds from multiple addresses and then randomly issuing them to other addresses, making it difficult to trace the funds.
Using NFTs as Money Laundering Tools: Some criminals are using Non–Fungible as a means of laundering money, by repeatedly buying or selling NFTs at their own set prices to transform illicit funds into legitimate-looking assets.
Prevention Tips
Implementation of KYC and AML on Exchange Platforms: Many crypto exchange platforms now implement Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations to verify user identities and prevent misuse of the system for money laundering.
Blockchain Monitoring Tools: Blockchain monitoring technology is used to detect suspicious transactions, such as large fund flows or transactions involving blacklisted addresses.
Real Case Studies: Real cases that reveal money laundering using cryptocurrencies include events such as cyberattacks on exchanges and cryptocurrency thefts, where perpetrators use techniques such as Over-the-Counter (OTC) brokers and mixers to obscure the origin of stolen funds.
Challenges of Law Enforcement in the Digital Era
Law enforcement in the digital era, especially related to money laundering through cryptocurrency, faces a number of complex challenges. Some of them are as follows:
1. Regulatory Gaps Between Countries
Regulations related to cryptocurrency still vary from country to country, with some countries not yet having clear or consistent rules.
This creates difficulties in effective law enforcement, especially when criminals move across national borders.
2. Technology Develops Faster Than Regulation
Blockchain and cryptocurrency technology are developing very rapidly, while regulations governing this technology often lag behind.
This makes it difficult for authorities to keep up with the rapid changes in the methods and tools used by criminals.
3. Difficulty Tracking Perpetrators Across Jurisdictions
Crimes involving cryptocurrency are often committed in different jurisdictions. This makes it difficult for authorities to track perpetrators or assets effectively, given the differences in laws and procedures in each country.
4. Lack of User Awareness of Money Laundering Risks in Crypto
Many cryptocurrency users are not fully aware of the potential money laundering risks associated with digital transactions.
This lack of education and understanding opens up opportunities for criminals to exploit cryptocurrency platforms in ways that are difficult to detect.
Conclusion
So, that was an interesting discussion about Money Laundry: Modes, Stages, and Prevention Methods that you can read in full at the Crypto Academy at INDODAX Academy.
In conclusion, preventing money laundering, especially involving cryptocurrency, requires close collaboration between the government, financial institutions, and technology providers.
In addition, more intensive public education is also very important to increase awareness of potential risks and how to prevent them.
Users also have a very important role in ensuring that their financial activities comply with applicable regulations and avoid practices that can harm the global financial system.
In the future, the development of more adaptive regulations and sophisticated technology will be important elements in combating money laundering and maintaining the integrity of the digital financial system.
FAQ
1. What is money laundering?
Money laundering is the process of hiding the origins of illegal funds to make them appear legitimate, usually carried out by criminals to avoid detection.
2. What are the stages of money laundering?
The stages of money laundering consist of placement, layering, and integration to hide or disguise the source of illegal funds.
3. What are the common modes of money laundering?
Modes of money laundering include the distribution of funds to other accounts, fictitious transactions, the use of shell companies, and investment in luxury goods.
4. How is cryptocurrency used in money laundering?
Cryptocurrency allows for anonymous and cross-border transactions, making it vulnerable to use in money laundering through methods such as mixers and tumblers.
5. What is the role of regulation in preventing money laundering?
Regulations such as Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) are expected to prevent money laundering by verifying user identities and monitoring suspicious transactions.





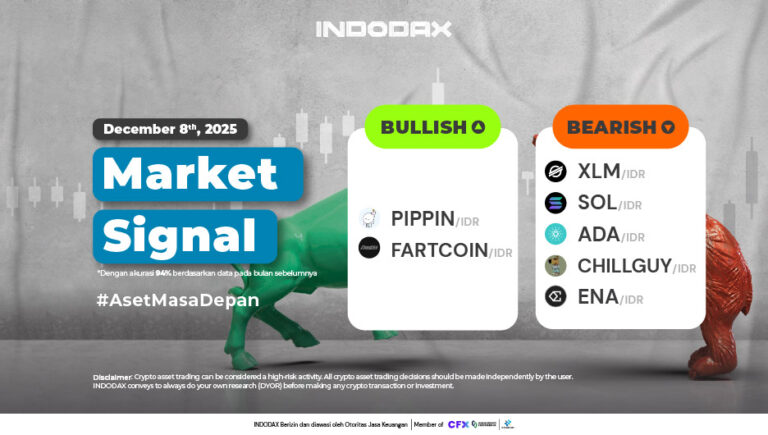
 Polkadot 9.66%
Polkadot 9.66%
 BNB 0.78%
BNB 0.78%
 Solana 4.89%
Solana 4.89%
 Ethereum 2.37%
Ethereum 2.37%
 Cardano 1.22%
Cardano 1.22%
 Polygon Ecosystem Token 2.16%
Polygon Ecosystem Token 2.16%
 Tron 2.84%
Tron 2.84%
 Market
Market